Recent Blackouts
Russia, 25 May 2005
A transformer exploded at Chagino 500 kV to 220 kV/110 kV substation at 9:17 pm 24 May. The operator decided to restore power from available capacity and lines. Power demand increased early in the morning leading to failure of third Chagino transformer at 5:31 am 25 May. Five power lines connected to Ochakovo substation have failed due to “short circuits” and sixth failed due to “overload” at 10:12 am 25 May, initiating automatic protection devices and cascading outages. Four out of seven Moscow electric power supply stations and 15 supply centres failed. Five Moscow power plants went of line. It took 32 hours to restore power to all customers.
english.peopledaily.com.cn/200505/26/eng20050526_186951.html
pserc.org/MoscowBlackout.htm
Italy, 28 September 2003 - Italian blackout was caused by contact between sagging OH-line conductors and growing trees. The contact resulted in a loss of transmission line between Italy and Switzerland. Neighbouring transmission circuits became overloaded and tripping of a seconds transmission line, 20 minutes later. This led to tripping of all interconnections in Italy and Switzerland. 58 million customers in Italy were affected by the blackout for 20 hours.
worldenergy.org/wec-geis/focus/blackouts/italy.asp
bfe.admin.ch/themen/00612/00619/index.html?lang=en
Southern Sweden and Eastern Denmark, 23 September 2003
Failure of a large generator unit resulted in loss of four transmission lines due to bus fault five minutes later. The remaining circuits became overloaded and tripped causing blackouts in Sweden and Denmark. It took six hours to restore power supply. 4 million people were affected in Sweden.
ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=1373158
United Kingdom, 28 August 2003
The blackout was caused by two faults, failure of transformer due to oil leak and fitting of the wrong part in the system. Transformer faults are typical, normally they switched off. However, the switching was prevented by the second cause of blackout. The transformer leak was spotted in March. The oil had been topped up but the transformer was not fixed in time to prevent the failure. Power supply was fully restored in two hours. The blackout affected 500,000 people in total,south and south-east London rail services, sixty percent of the London Underground. They have shut down its last independent generator in 2002, and 270 sets of traffic lights.
news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/london/3189755.stm
worldenergy.org/wec-geis/focus/blackouts/london.asp
North America, 14 August 2003
Blackout was caused by contact between sagging OH-line conductors and growing trees. The contact caused a tripping of a major transmission line, thus resulting in overload of remaining transmission lines. System operators were distracted by monitoring system and alarms triggered by failures. 60,000 MW of load power was lost. Restoration of full power supply took 8 days. Overload was also caused by poor communication with system operators in neighbouring regions.

Toronto during the blackout [Wikipedia]
Rise in power demand is caused by a shift in generator frequencies:
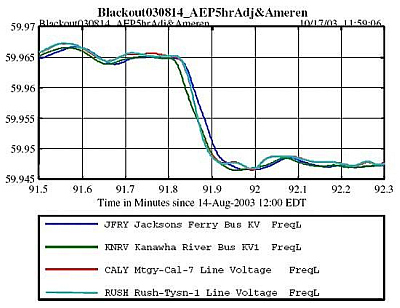
Frequency drifts at 13:31 EDT, 0.2 Hz filter applied to smooth the data
The blackout results in a loss of power in northern eastern US and south eastern Canadian states. 50 million people were affected. semp.us/biots/biot_391.html
